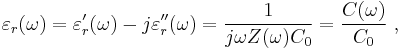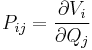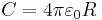Capacitance
| Electromagnetism |
|---|
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored (or separated) for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor. In a parallel plate capacitor, capacitance is directly proportional to the surface area of the conductor plates and inversely proportional to the separation distance between the plates. If the charges on the plates are +q and −q, and V gives the voltage between the plates, then the capacitance is given by
The SI unit of capacitance is the farad; 1 farad is 1 coulomb per volt.
The energy (measured in joules) stored in a capacitor is equal to the work done to charge it. Consider a capacitor of capacitance C, holding a charge +q on one plate and −q on the other. Moving a small element of charge dq from one plate to the other against the potential difference V = q/C requires the work dW:
where W is the work measured in joules, q is the charge measured in coulombs and C is the capacitance, measured in farads.
The energy stored in a capacitor is found by integrating this equation. Starting with an uncharged capacitance (q = 0) and moving charge from one plate to the other until the plates have charge +Q and −Q requires the work W:
Contents |
Capacitors
The capacitance of the majority of capacitors used in electronic circuits is several orders of magnitude smaller than the farad. The most common subunits of capacitance in use today are the millifarad (mF), microfarad (µF), nanofarad (nF), picofarad (pF), and femtofarad (fF).
Capacitance can be calculated if the geometry of the conductors and the dielectric properties of the insulator between the conductors are known. For example, the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor constructed of two parallel plates both of area A separated by a distance d is approximately equal to the following:
where
- C is the capacitance;
- A is the area of overlap of the two plates;
- εr is the relative static permittivity (sometimes called the dielectric constant) of the material between the plates (for a vacuum, εr = 1);
- ε0 is the electric constant (ε0 ≈ 8.854×10−12 F m–1); and
- d is the separation between the plates.
Capacitance is proportional to the area of overlap and inversely proportional to the separation between conducting sheets. The closer the sheets are to each other, the greater the capacitance. The equation is a good approximation if d is small compared to the other dimensions of the plates so the field in the capacitor over most of its area is uniform, and the so-called fringing field around the periphery provides a small contribution. In CGS units the equation has the form:[1]
where C in this case has the units of length. Combining the SI equation for capacitance with the above equation for the energy stored in a capacitance, for a flat-plate capacitor the energy stored is:
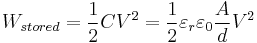 .
.
where W is the energy, in joules; C is the capacitance, in farads; and V is the voltage, in volts.
Voltage dependent capacitors
The dielectric constant for a number of very useful dielectrics changes as a function of the applied electrical field, for example ferroelectric materials, so the capacitance for these devices is more complex. For example, in charging such a capacitor the differential increase in voltage with charge is governed by:
where the voltage dependence of capacitance, C(V), stems from the field, which in a large area parallel plate device is given by ε = V/d. This field polarizes the dielectric, which polarization, in the case of a ferroelectric, is a nonlinear S-shaped function of field, which, in the case of a large area parallel plate device, translates into a capacitance that is a nonlinear function of the voltage causing the field.[2][3]
Corresponding to the voltage-dependent capacitance, to charge the capacitor to voltage V an integral relation is found:
which agrees with Q = CV only when C is voltage independent.
By the same token, the energy stored in the capacitor now is given by
Integrating:
where interchange of the order of integration is used.
The nonlinear capacitance of a microscope probe scanned along a ferroelectric surface is used to study the domain structure of ferroelectric materials.[4]
Another example of voltage dependent capacitance occurs in semiconductor devices such as semiconductor diodes, where the voltage dependence stems not from a change in dielectric constant but in a voltage dependence of the spacing between the charges on the two sides of the capacitor.[5]
Frequency dependent capacitors
If a capacitor is driven with a time-varying voltage that changes rapidly enough, then the polarization of the dielectric cannot follow the signal. As an example of the origin of this mechanism, the internal microscopic dipoles contributing to the dielectric constant cannot move instantly, and so as frequency of an applied alternating voltage increases, the dipole response is limited and the dielectric constant diminishes. A changing dielectric constant with frequency is referred to as dielectric dispersion, and is governed by dielectric relaxation processes, such as Debye relaxation. Under transient conditions, the displacement field can be expressed as (see electric susceptibility):
indicating the lag in response by the time dependence of εr, calculated in principle from an underlying microscopic analysis, for example, of the dipole behavior in the dielectric. See, for example, linear response function.[6][7] The integral extends over the entire past history up to the present time. A Fourier transform in time then results in:
where εr(ω) is now a complex function, with an imaginary part related to absorption of energy from the field by the medium. See permittivity. The capacitance, being proportional to the dielectric constant, also exhibits this frequency behavior. Fourier transforming Gauss's law with this form for displacement field:
where j is the imaginary unit, V(ω) is the voltage component at angular frequency ω, G(ω) is the real part of the current, called the conductance, and C(ω) determines the imaginary part of the current and is the capacitance. Z(ω) is the complex impedance.
When a parallel-plate capacitor is filled with a dielectric, the measurement of dielectric properties of the medium is based upon the relation:
where a single prime denotes the real part and a double prime the imaginary part, Z(ω) is the complex impedance with the dielectric present, C(ω) is the so-called complex capacitance with the dielectric present, and C0 is the capacitance without the dielectric.[8][9] (Measurement "without the dielectric" in principle means measurement in free space, an unattainable goal inasmuch as even the quantum vacuum is predicted to exhibit nonideal behavior, such as dichroism. For practical purposes, when measurement errors are taken into account, often a measurement in terrestrial vacuum, or simply a calculation of C0, is sufficiently accurate.[10])
Using this measurement method, the dielectric constant may exhibit a resonance at certain frequencies corresponding to characteristic response frequencies (excitation energies) of contributors to the dielectric constant. These resonances are the basis for a number of experimental techniques for detecting defects. The conductance method measures absorption as a function of frequency.[11] Alternatively, the time response of the capacitance can be used directly, as in deep-level transient spectroscopy.[12]
Another example of frequency dependent capacitance occurs with MOS capacitors, where the slow generation of minority carriers means that at high frequencies the capacitance measures only the majority carrier response, while at low frequencies both types of carrier respond.[13][14]
At optical frequencies, in semiconductors the dielectric constant exhibits structure related to the band structure of the solid. Sophisticated modulation spectroscopy measurement methods based upon modulating the crystal structure by pressure or by other stresses and observing the related changes in absorption or reflection of light have advanced our knowledge of these materials.[15]
Capacitance matrix
The discussion above is limited to the case of two conducting plates, although of arbitrary size and shape. The definition C=Q/V still holds for a single plate given a charge, in which case the field lines produced by that charge terminate as if the plate were at the center of an oppositely charged sphere at infinity.
 does not apply when there are more than two charged plates, or when the net charge on the two plates is non-zero. To handle this case, Maxwell introduced his coefficients of potential. If three plates are given charges
does not apply when there are more than two charged plates, or when the net charge on the two plates is non-zero. To handle this case, Maxwell introduced his coefficients of potential. If three plates are given charges 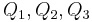 , then the voltage of plate 1 is given by
, then the voltage of plate 1 is given by
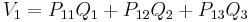 ,
,
and similarly for the other voltages. Hermann von Helmholtz and Sir William Thomson showed that the coefficients of potential are symmetric, so that 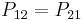 , etc. Thus the system can be described by a collection of coefficients known as the elastance matrix or reciprocal capacitance matrix, which is defined as:
, etc. Thus the system can be described by a collection of coefficients known as the elastance matrix or reciprocal capacitance matrix, which is defined as:
From this, the mutual capacitance 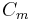 between two objects can be defined[16] by solving for the total charge Q and using
between two objects can be defined[16] by solving for the total charge Q and using 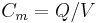 .
.
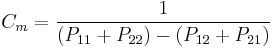
Since no actual device holds perfectly equal and opposite charges on each of the two "plates", it is the mutual capacitance that is reported on capacitors.
The collection of coefficients 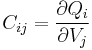 is known as the capacitance matrix,[17][18] and is the inverse of the elastance matrix.
is known as the capacitance matrix,[17][18] and is the inverse of the elastance matrix.
Self-capacitance
In electrical circuits, the term capacitance is usually a shorthand for the mutual capacitance between two adjacent conductors, such as the two plates of a capacitor. However, for an isolated conductor there also exists a property called self-capacitance, which is the amount of electrical charge that must be added to an isolated conductor to raise its electrical potential by one unit (i.e. one volt, in most measurement systems).[19] The reference point for this potential is a theoretical hollow conducting sphere, of infinite radius, centered on the conductor. Using this method, the self-capacitance of a conducting sphere of radius R is given by:[20]
Example values of self-capacitance are:
- for the top "plate" of a van de Graaff generator, typically a sphere 20 cm in radius: 20 pF
- the planet Earth: about 710 µF[21]
The capacitative component of a coil, which reduces its impedance at high frequencies and can lead to resonance and self-oscillation, is also called self-capacitance[22] as well as stray or parasitic capacitance.
Elastance
The reciprocal of capacitance is called elastance. The unit of elastance is the daraf, but is not recognised by SI.
Stray capacitance
Any two adjacent conductors can be considered a capacitor, although the capacitance will be small unless the conductors are close together for long. This (often unwanted) effect is termed "stray capacitance". Stray capacitance can allow signals to leak between otherwise isolated circuits (an effect called crosstalk), and it can be a limiting factor for proper functioning of circuits at high frequency.
Stray capacitance is often encountered in amplifier circuits in the form of "feedthrough" capacitance that interconnects the input and output nodes (both defined relative to a common ground). It is often convenient for analytical purposes to replace this capacitance with a combination of one input-to-ground capacitance and one output-to-ground capacitance. (The original configuration — including the input-to-output capacitance — is often referred to as a pi-configuration.) Miller's theorem can be used to effect this replacement. Miller's theorem states that, if the gain ratio of two nodes is 1/K, then an impedance of Z connecting the two nodes can be replaced with a Z/(1-k) impedance between the first node and ground and a KZ/(K-1) impedance between the second node and ground. (Since impedance varies inversely with capacitance, the internode capacitance, C, will be seen to have been replaced by a capacitance of KC from input to ground and a capacitance of (K-1)C/K from output to ground.) When the input-to-output gain is very large, the equivalent input-to-ground impedance is very small while the output-to-ground impedance is essentially equal to the original (input-to-output) impedance.
Capacitance of simple systems
Calculating the capacitance of a system amounts to solving the Laplace equation ∇2φ=0 with a constant potential φ on the surface of the conductors. This is trivial in cases with high symmetry. There is no solution in terms of elementary functions in more complicated cases.
For quasi two-dimensional situations analytic functions may be used to map different geometries to each other. See also Schwarz-Christoffel mapping.
| Type | Capacitance | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel-plate capacitor | 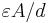 |
A: Area d: Distance ε: Permittivity |
| Coaxial cable | 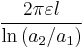 |
a1: Inner radius a2: Outer radius 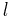 : Length : Length |
| Pair of parallel wires[23] | 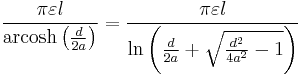 |
a: Wire radius d: Distance, d > 2a 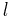 : Length of pair : Length of pair |
| Wire parallel to wall[23] | 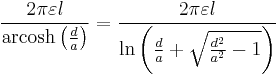 |
a: Wire radius d: Distance, d > a 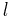 : Wire length : Wire length |
| Two parallel coplanar strips[24] |
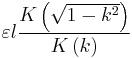 |
d: Distance w1, w2: Strip width ki: d/(2wi+d) k2: k1k2 |
| Concentric spheres | 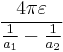 |
a1: Inner radius a2: Outer radius |
| Two spheres, equal radius[25][26] |
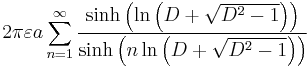 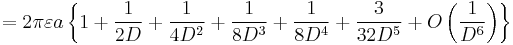 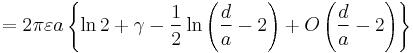 |
a: Radius d: Distance, d > 2a D = d/2a γ: Euler's constant |
| Sphere in front of wall[25] | 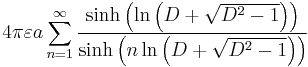 |
a: Radius d: Distance, d > a D = d/a |
| Sphere | 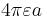 |
a: Radius |
| Circular disc[27] | 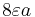 |
a: Radius |
| Thin straight wire, finite length[28][29][30] |
![\frac{2\pi \varepsilon l}{\Lambda }\left\{ 1%2B\frac{1}{\Lambda }\left( 1-\ln 2\right) %2B\frac{1}{\Lambda ^{2}}\left[ 1%2B\left( 1-\ln 2\right) ^{2}-\frac{\pi ^{2}}{12}\right] %2BO\left(\frac{1}{\Lambda ^{3}}\right) \right\}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8ed16f312307e41ae8adbc3394ac0cdc.png) |
a: Wire radius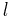 : Length : LengthΛ: ln( 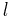 /a) /a) |
See also
References
- ^ The Physics Problem Solver, 1986, Google books link
- ^ Carlos Paz de Araujo, Ramamoorthy Ramesh, George W Taylor (Editors) (2001). Science and Technology of Integrated Ferroelectrics: Selected Papers from Eleven Years of the Proceedings of the International Symposium on Integrated Ferroelectrics. CRC Press. Figure 2, p. 504. ISBN 9056997041. http://books.google.com/books?id=QMlOkeJ4qN4C&pg=PA504&dq=nonlinear+capacitance+ferroelectric&lr=&as_brr=0.
- ^ Solomon Musikant (1991). What Every Engineer Should Know about Ceramics. CRC Press. Figure 3.9, p. 43. ISBN 0824784987. http://books.google.com/books?id=Jc8xRdgdH38C&pg=PA44&dq=nonlinear+capacitance+ferroelectric&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA43,M1.
- ^ Yasuo Cho (2005). Scanning Nonlinear Dielectric Microscope (in Polar Oxides; R Waser, U Böttger & S Tiedke, editors ed.). Wiley-VCH. Chapter 16. ISBN 3527405321. http://books.google.com/books?id=wQ09DhMBJroC&pg=PA304&dq=nonlinear+capacitance+ferroelectric&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA303,M1.
- ^ Simon M. Sze, Kwok K. Ng (2006). Physics of Semiconductor Devices (3rd Edition ed.). Wiley. Figure 25, p. 121. ISBN 0470068302. http://books.google.com/books?id=o4unkmHBHb8C&pg=PA217&dq=high+low+frequency+C-V&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA121,M1.
- ^ Gabriele Giuliani, Giovanni Vignale (2005). Quantum Theory of the Electron Liquid. Cambridge University Press. p. 111. ISBN 0521821126. http://books.google.com/books?id=kFkIKRfgUpsC&pg=PA538&dq=%22linear+response+theory%22+capacitance+OR+conductance&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA111,M1.
- ^ Jørgen Rammer (2007). Quantum Field Theory of Non-equilibrium States. Cambridge University Press. p. 158. ISBN 0521874998. http://books.google.com/books?id=A7TbrAm5Wq0C&pg=PR6&dq=%22linear+response+theory%22+capacitance+OR+conductance&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA158,M1.
- ^ Horst Czichos, Tetsuya Saito, Leslie Smith (2006). Springer Handbook of Materials Measurement Methods. Springer. p. 475. ISBN 3540207856. http://books.google.com/books?id=8lANaR-Pqi4C&pg=RA1-PA475&dq=%22the+dielectric+permittivity+is+defined%22&lr=&as_brr=0.
- ^ William Coffey, Yu. P. Kalmykov (2006). Fractals, diffusion and relaxation in disordered complex systems..Part A. Wiley. p. 17. ISBN 0470046074. http://books.google.com/books?id=mgtQslaXBc4C&pg=PA18&dq=%22dielectric+relaxation+function%22&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA17,M1.
- ^ J. Obrzut, A. Anopchenko and R. Nozaki, "Broadband Permittivity Measurements of High Dielectric Constant Films", Proceedings of the IEEE: Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, 2005, pp.1350-1353, 16-19 May 2005, Ottawa ISBN 0-7803-8879-8 doi:10.1109/IMTC.2005.1604368
- ^ Dieter K Schroder (2006). Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization (3rd Edition ed.). Wiley. p. 347 ff.. ISBN 0471739065. http://books.google.com/books?id=OX2cHKJWCKgC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA347,M1.
- ^ Dieter K Schroder (2006). Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization (3rd Edition ed.). Wiley. p. 270 ff.. ISBN 0471739065. http://books.google.com/books?id=OX2cHKJWCKgC&pg=PA305&dq=capacitance+conductance+measurement+spectroscopy&lr=&as_brr=0#PPA271,M1.
- ^ Simon M. Sze, Kwok K. Ng (2006). Physics of Semiconductor Devices (3rd Edition ed.). Wiley. p. 217. ISBN 0470068302. http://books.google.com/books?id=o4unkmHBHb8C&pg=PA217&dq=high+low+frequency+C-V&lr=&as_brr=0.
- ^ Safa O. Kasap, Peter Capper (2006). Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials. Springer. Figure 20.22, p. 425. http://books.google.com/books?id=rVVW22pnzhoC&pg=PA425&dq=high+low+frequency+C-V&lr=&as_brr=0.
- ^ PY Yu and Manuel Cardona (2001). Fundamentals of Semiconductors (3rd Edition ed.). Springer. p. §6.6 Modulation Spectroscopy. ISBN 3540254706. http://books.google.com/books?id=W9pdJZoAeyEC&pg=PA244&dq=isbn=3540254706#PPA315,M1.
- ^ Jackson, John David (1999), Classical Electrodynamic (3rd. ed.), USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 43, ISBN 978-0-471-30932-1
- ^ Maxwell, James (1873), "3", A treatise on electricity and magnetism, Volume 1, Clarendon Press, pp. 88ff, http://www.archive.org/details/electricandmagne01maxwrich
- ^ "Capacitance". http://www.av8n.com/physics/capacitance.htm. Retrieved 20 September 2010.
- ^ William D. Greason (1992). Electrostatic discharge in electronics. Research Studies Press. p. 48. ISBN 978-0-86380-136-5. http://books.google.com/books?id=404fAQAAIAAJ. Retrieved 4 December 2011.
- ^ Lecture notes; University of New South Wales
- ^ Tipler, Paul; Mosca, Gene (2004), Physics for scientists and engineers (5th ed.), Macmillan, p. 752, ISBN 9780716708100
- ^ Massarini, A.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. (1997). "Self-capacitance of inductors". IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 12 (4): 671-676. doi:10.1109/63.602562.: example of use of term self-capacitance
- ^ a b Jackson, J. D. (1975). Classical Electrodynamics. Wiley. p. 80.
- ^ Binns; Lawrenson (1973). Analysis and computation of electric and magnetic field problems. Pergamon Press. ISBN 978-0-08-016638-4.
- ^ a b Maxwell, J. C. (1873). A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism. Dover. pp. 266 ff. ISBN 0-486-60637-6.
- ^ Rawlins, A. D. (1985). "Note on the Capacitance of Two Closely Separated Spheres". IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics 34 (1): 119–120. doi:10.1093/imamat/34.1.119.
- ^ Jackson, J. D. (1975). Classical Electrodynamics. Wiley. p. 128, problem 3.3.
- ^ Maxwell, J. C. (1878). "On the electrical capacity of a long narrow cylinder and of a disk of sensible thickness". Proc. London Math. Soc. IX: 94–101. doi:10.1112/plms/s1-9.1.94.
- ^ Vainshtein, L. A. (1962). "Static boundary problems for a hollow cylinder of finite length. III Approximate formulas". Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 32: 1165–1173.
- ^ Jackson, J. D. (2000). "Charge density on thin straight wire, revisited". Am. J. Phys 68 (9): 789–799. Bibcode 2000AmJPh..68..789J. doi:10.1119/1.1302908.
Further reading
- Tipler, Paul (1998). Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Vol. 2: Electricity and Magnetism, Light (4th ed.). W. H. Freeman. ISBN 1-57259-492-6
- Serway, Raymond; Jewett, John (2003). Physics for Scientists and Engineers (6 ed.). Brooks Cole. ISBN 0-534-40842-7
- Saslow, Wayne M.(2002). Electricity, Magnetism, and Light. Thomson Learning. ISBN 0-12-619455-6. See Chapter 8, and especially pp. 255–259 for coefficients of potential.
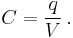
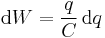
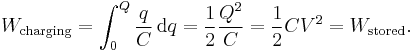
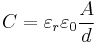
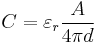
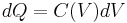
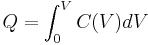
![dW =Q dV =\left[ \int_0^V\ dV' \ C(V') \right] \ dV \ .](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/22c8e7f9c2fada07ec3e7b5db9595335.png)
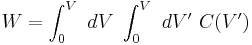
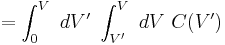
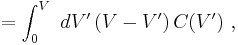
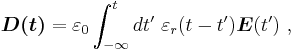
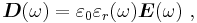
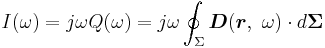
![=\left[ G(\omega) %2B j \omega C(\omega)\right] V(\omega) = \frac {V(\omega)}{Z(\omega)} \ ,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/1c26e3058faebae777f003bea8718a9a.png)